 A Sept. 30 Associated Press story that got wide play in Northern California and the Pacific Northwest marked another concern about the ecological impacts of outdoor cannabis grows in the Emerald Traingle. The NOAA Fisheries Service in its new coho salmon recovery plan for the Northern California and Southern Oregon region finds that water use by the marijuana industry further threatens salmon already in danger of extinction. The plan calls for determining and decreasing the amount of water that growers illegally withdraw from creeks where young fish struggle to survive. Other threats from the unregulated industry include clear-cutting to make way for grows, punching roads that send sediment into streams, and use of fertilizer and pesticides that poison waters. Coho salmon have been listed as a threatened species since 1997, due to loss of habitat from logging, agriculture, urban development and dams, as well as overfishing—issues also addressed in the recovery plan. The highlighting of cannabis stems from a California Department of Fish and Wildlife study that said growers suck millions of gallons of water from salmon streams.
A Sept. 30 Associated Press story that got wide play in Northern California and the Pacific Northwest marked another concern about the ecological impacts of outdoor cannabis grows in the Emerald Traingle. The NOAA Fisheries Service in its new coho salmon recovery plan for the Northern California and Southern Oregon region finds that water use by the marijuana industry further threatens salmon already in danger of extinction. The plan calls for determining and decreasing the amount of water that growers illegally withdraw from creeks where young fish struggle to survive. Other threats from the unregulated industry include clear-cutting to make way for grows, punching roads that send sediment into streams, and use of fertilizer and pesticides that poison waters. Coho salmon have been listed as a threatened species since 1997, due to loss of habitat from logging, agriculture, urban development and dams, as well as overfishing—issues also addressed in the recovery plan. The highlighting of cannabis stems from a California Department of Fish and Wildlife study that said growers suck millions of gallons of water from salmon streams.
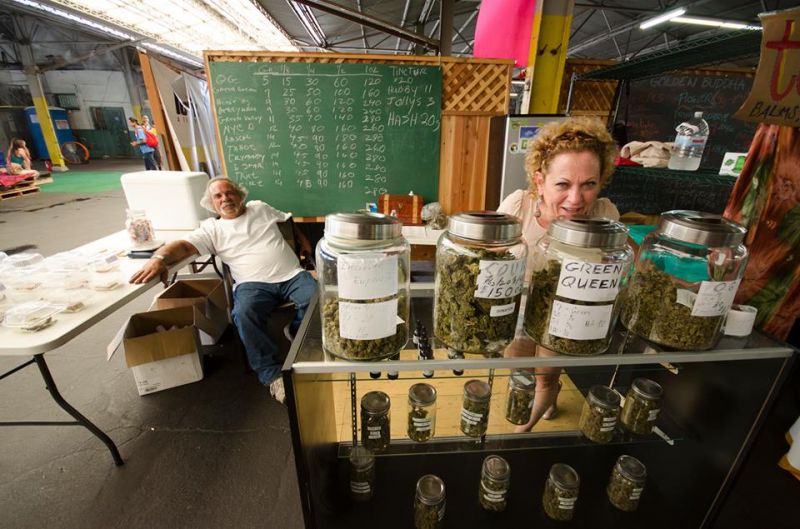
 Los Angeles' first-ever marijuana farmers market was
Los Angeles' first-ever marijuana farmers market was  In an unprecedented 219-189 floor vote late May 29, the House of Representatives approved the end of funding for Department of Justice (DoJ) enforcement in medical marijuana states. Advocates are hailing the vote as a major victory that signals a shift in the approach Congress is taking on this issue. The vote was on Amendment No. 25 to the Commerce, Justice & Science (CJS) appropriations bill. One hundred seventy Democrats and 49 Republicans voted in favor of the amendment. "This Congressional vote is a huge victory for patients," said Steph Sherer, executive director of Americans for Safe Access. "No longer will we have to look over our shoulder and worry when the next raid or indictment will prevent us from safely and legally accessing our medicine. This is a game-changer that paves the way for much more policy change to come."
In an unprecedented 219-189 floor vote late May 29, the House of Representatives approved the end of funding for Department of Justice (DoJ) enforcement in medical marijuana states. Advocates are hailing the vote as a major victory that signals a shift in the approach Congress is taking on this issue. The vote was on Amendment No. 25 to the Commerce, Justice & Science (CJS) appropriations bill. One hundred seventy Democrats and 49 Republicans voted in favor of the amendment. "This Congressional vote is a huge victory for patients," said Steph Sherer, executive director of Americans for Safe Access. "No longer will we have to look over our shoulder and worry when the next raid or indictment will prevent us from safely and legally accessing our medicine. This is a game-changer that paves the way for much more policy change to come."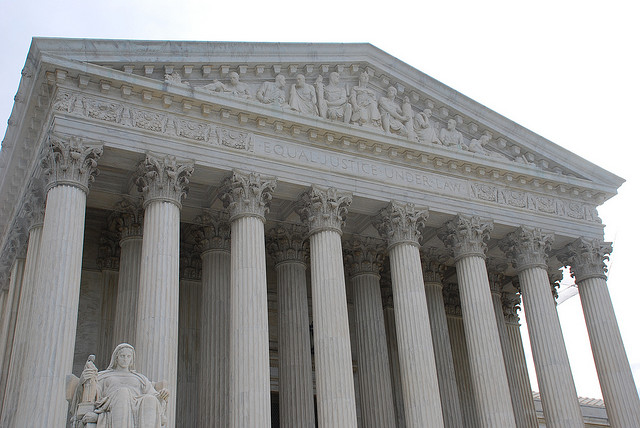 The US Supreme Court ruled 5-4 on April 22 in Navarette v. California that a traffic stop that led to a marijuana arrest was constitutional because police had reasonable suspicion the driver was intoxicated. In 2008, California Highway Patrol officers stopped Lorenzo Prado Navarette's pickup truck on a Mendocino County road based on a 911 tip about reckless driving. The officers said they smelled marijuana when approaching the vehicle. They conducted a search and found 30 pounds of cannabis. Navarette and a passenger were arrested and charged. At trial, they moved to suppress the evidence on grounds that the search violated their Fourth Amendment rights because the officers lacked reasonable suspicion when they pulled Navarette over. But in the opinion authored by conservative Justice Clarence Thomas, the majority found that while an anonymous tip will not always lead to reasonable suspicion, in this case it did. The court found that "under appropriate circumstances, an anonymous tip can demonstrate sufficient indicia of reliability to provide reasonable suspicion to make an investigatory stop." Conservative Justice Antonin Scalia wrote a dissent that was joined by the court's liberals, Ruth Bader Ginsburg, Sonia Sotomayor and Elena Kagan. Conservatives John Roberts and Samuel Alito lined up with the majority, as did swing voters Stephen Breyer and Anthony Kennedy. (
The US Supreme Court ruled 5-4 on April 22 in Navarette v. California that a traffic stop that led to a marijuana arrest was constitutional because police had reasonable suspicion the driver was intoxicated. In 2008, California Highway Patrol officers stopped Lorenzo Prado Navarette's pickup truck on a Mendocino County road based on a 911 tip about reckless driving. The officers said they smelled marijuana when approaching the vehicle. They conducted a search and found 30 pounds of cannabis. Navarette and a passenger were arrested and charged. At trial, they moved to suppress the evidence on grounds that the search violated their Fourth Amendment rights because the officers lacked reasonable suspicion when they pulled Navarette over. But in the opinion authored by conservative Justice Clarence Thomas, the majority found that while an anonymous tip will not always lead to reasonable suspicion, in this case it did. The court found that "under appropriate circumstances, an anonymous tip can demonstrate sufficient indicia of reliability to provide reasonable suspicion to make an investigatory stop." Conservative Justice Antonin Scalia wrote a dissent that was joined by the court's liberals, Ruth Bader Ginsburg, Sonia Sotomayor and Elena Kagan. Conservatives John Roberts and Samuel Alito lined up with the majority, as did swing voters Stephen Breyer and Anthony Kennedy. ( Four kayakers attempting to smuggle nearly 300 pounds of cannabis into the US were arrested at sea on the morning of Nov. 22, federal authorities announced. US
Four kayakers attempting to smuggle nearly 300 pounds of cannabis into the US were arrested at sea on the morning of Nov. 22, federal authorities announced. US 





Recent comments
5 days 21 hours ago
6 days 4 hours ago
3 weeks 6 days ago
4 weeks 6 days ago
8 weeks 6 days ago
12 weeks 4 days ago
16 weeks 5 days ago
17 weeks 3 days ago
27 weeks 3 days ago
31 weeks 3 days ago