Posted on February 1st, 2021 by Bill Weinberg and tagged
California,
capitalism,
China,
Colorado,
features,
Georgia,
Germany,
hemp,
Iowa,
Native America,
New England,
North Dakota,
Planet Watch,
science,
Switzerland,
United States,
Wisconsin.
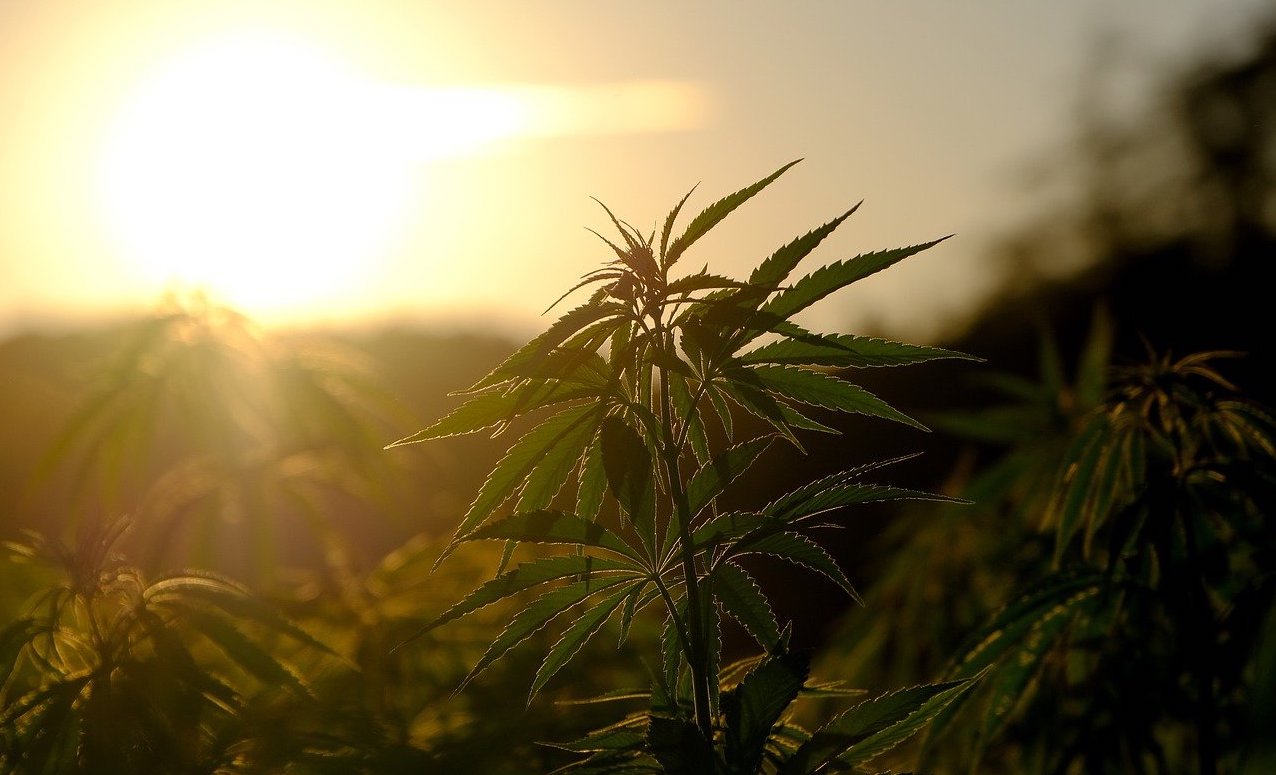 What will Biden’s Agriculture Department Mean for Small Farmers and Hemp?
What will Biden’s Agriculture Department Mean for Small Farmers and Hemp?
Progressives coast to coast breathed a heavy sigh of relief as Joe Biden took the oath of office, ending the turbulent and reactionary rule of Donald Trump over the past four years.
But hemp cultivation, like the rewriting and replacement of NAFTA, was one of the few areas that actually saw positive change in the Trump years—with bipartisan support. The 2018 Farm Bill that re-legalized the crop after generations of prohibition bore Trump’s signature.
And there are fears that Biden could mean a return to the Washington consensus of a corporate-friendly “free trade” status quo ante, shorn even of the limited populist measures of the Trump era.
For small farmers, including some hemp cultivators, Biden’s choice to lead the US Department of Agriculture (USDA) may provide a case in point.
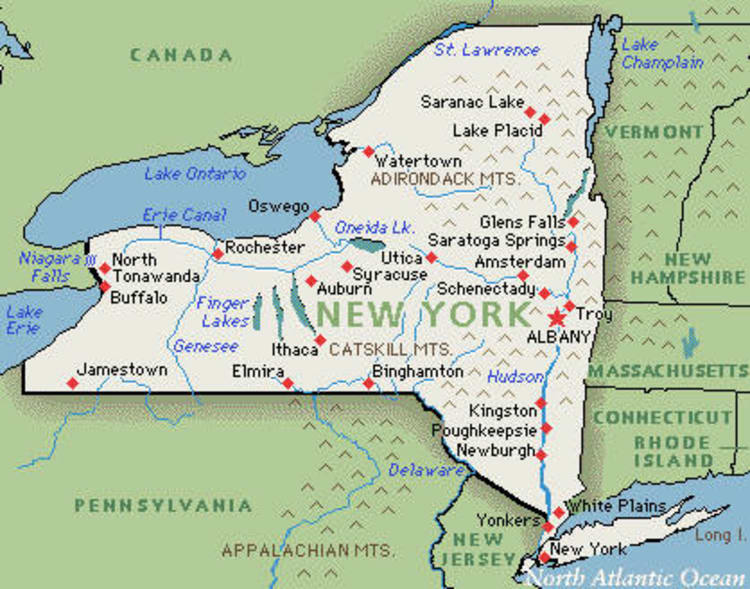 After years of activist effort, New York state finally passed the Marijuana Regulation & Taxation Act (MRTA), signed into law by a politically besieged Gov. Andrew Cuomo. This is being hailed as a victory by advocates, who pledge to craft a model of legalization that will dismantle a long legacy of racism and oppression under the prohibition regime.
After years of activist effort, New York state finally passed the Marijuana Regulation & Taxation Act (MRTA), signed into law by a politically besieged Gov. Andrew Cuomo. This is being hailed as a victory by advocates, who pledge to craft a model of legalization that will dismantle a long legacy of racism and oppression under the prohibition regime.
 What will Biden’s Agriculture Department Mean for Small Farmers and Hemp?
What will Biden’s Agriculture Department Mean for Small Farmers and Hemp?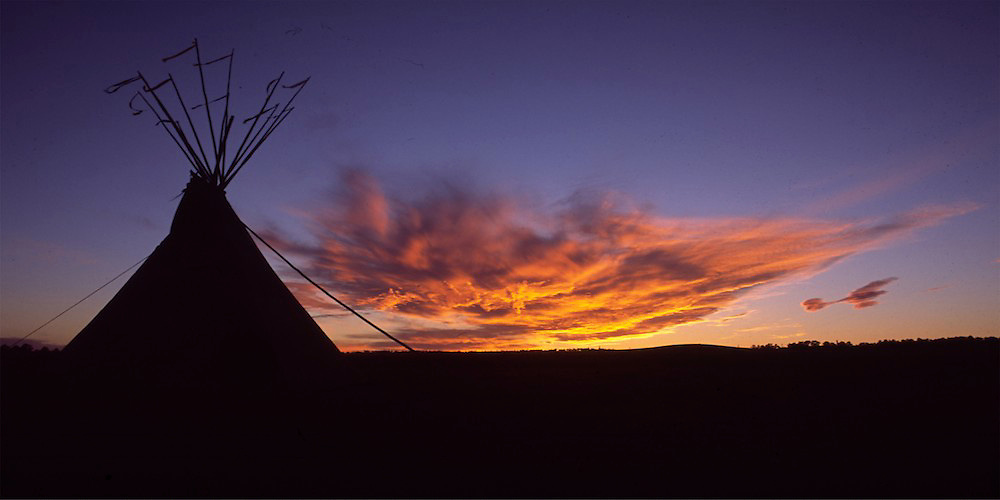 The original peoples of what is now the United States were left in legal limbo in the wake of the 2018 Farm Bill, which made hemp cultivation again lawful. Federally recognized Native American tribes could not cultivate under state regulation, because the states have limited jurisdiction on their reservations. But the US Agriculture Department dragged its heels in issuing federal regs that could apply on these lands. Caught between two sovereigns, many farmers in Indian country are asserting their right to cultivate hemp under the un-extinguished sovereignty of their own Native nations.
The original peoples of what is now the United States were left in legal limbo in the wake of the 2018 Farm Bill, which made hemp cultivation again lawful. Federally recognized Native American tribes could not cultivate under state regulation, because the states have limited jurisdiction on their reservations. But the US Agriculture Department dragged its heels in issuing federal regs that could apply on these lands. Caught between two sovereigns, many farmers in Indian country are asserting their right to cultivate hemp under the un-extinguished sovereignty of their own Native nations. Voters in Arizona, Mississippi, Montana, New Jersey, Oregon and South Dakota passed statewide ballot measures favoring medical marijuana, adult-use cannabis legalization or hemp cultivation in the Nov. 3 elections.
Voters in Arizona, Mississippi, Montana, New Jersey, Oregon and South Dakota passed statewide ballot measures favoring medical marijuana, adult-use cannabis legalization or hemp cultivation in the Nov. 3 elections. Lebanon, long the Middle East's heartland of hashish, has legalized cannabis cultivation for the medical market—but before the law has even taken effect, rumblings of cynicism are heard from the country's traditional growers. The outlaw growers in the Bekaa Valley, with its centuries-long tradition of hash production, will likely remain illicit and face continued militarized enforcement—while corporate producers with state-of-the-art greenhouses on the urbanized coast dominate the industry. And the hashish market has been hard hit by the country's deep economic crisis, leaving the Bekaa cannabis farmers struggling.
Lebanon, long the Middle East's heartland of hashish, has legalized cannabis cultivation for the medical market—but before the law has even taken effect, rumblings of cynicism are heard from the country's traditional growers. The outlaw growers in the Bekaa Valley, with its centuries-long tradition of hash production, will likely remain illicit and face continued militarized enforcement—while corporate producers with state-of-the-art greenhouses on the urbanized coast dominate the industry. And the hashish market has been hard hit by the country's deep economic crisis, leaving the Bekaa cannabis farmers struggling.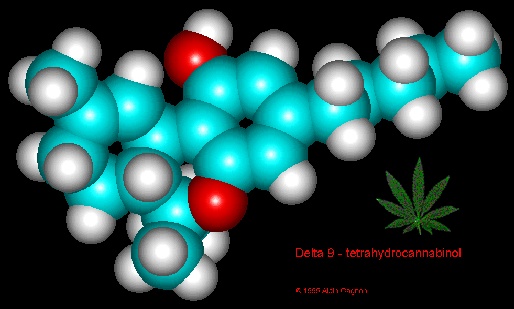 CBD products are now everywhere—health-food emporia, pharmacies, truck-stops. And pursuant to the 2018 Farm Bill, they are now legal—as long as the CBD is derived from “hemp” as opposed to what has traditionally been called “marijuana.” Hemp, as legally defined, is cannabis with under 0.3% THC—the psychoactive component of the plant, responsible for the long-stigmatized “high.”
CBD products are now everywhere—health-food emporia, pharmacies, truck-stops. And pursuant to the 2018 Farm Bill, they are now legal—as long as the CBD is derived from “hemp” as opposed to what has traditionally been called “marijuana.” Hemp, as legally defined, is cannabis with under 0.3% THC—the psychoactive component of the plant, responsible for the long-stigmatized “high.”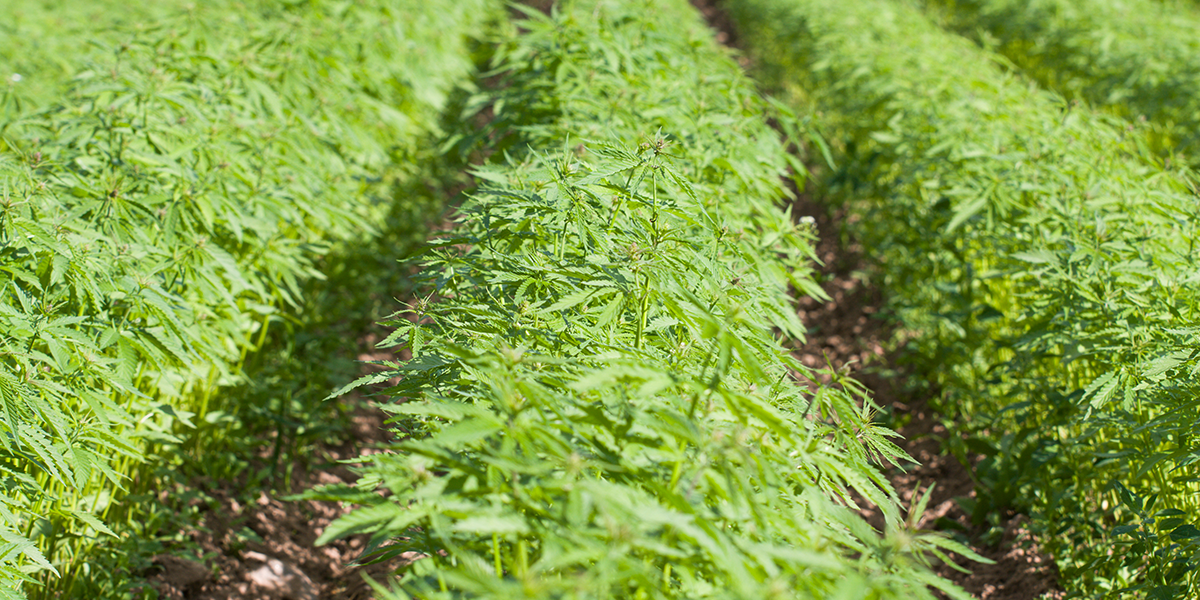 The autumn of 2019 saw the United States' first hemp harvest since effective prohibition of the crop under the strictures of the Marihuana Tax Act in 1937. These strictures were overturned in the Farm Bill signed into law by President Trump in the closing days of 2018. This harvest was looked to eagerly across much of rural America, as legal hemp had been plugged as a salvation for the nation's struggling farmers—and the soaring popularity of CBD appeared to provide a booming market. The fashionable cannabinoid had also been legalized by the 2018 Farm Bill—when derived from hemp, or cannabis with less than 0.3% THC.
The autumn of 2019 saw the United States' first hemp harvest since effective prohibition of the crop under the strictures of the Marihuana Tax Act in 1937. These strictures were overturned in the Farm Bill signed into law by President Trump in the closing days of 2018. This harvest was looked to eagerly across much of rural America, as legal hemp had been plugged as a salvation for the nation's struggling farmers—and the soaring popularity of CBD appeared to provide a booming market. The fashionable cannabinoid had also been legalized by the 2018 Farm Bill—when derived from hemp, or cannabis with less than 0.3% THC. Hemp’s Curious Cultural Trajectory
Hemp’s Curious Cultural Trajectory 





Recent comments
2 weeks 4 days ago
2 weeks 4 days ago
5 weeks 5 days ago
6 weeks 4 days ago
10 weeks 5 days ago
14 weeks 3 days ago
18 weeks 3 days ago
19 weeks 2 days ago
29 weeks 2 days ago
33 weeks 2 days ago